
Ovarian Cancer Facts
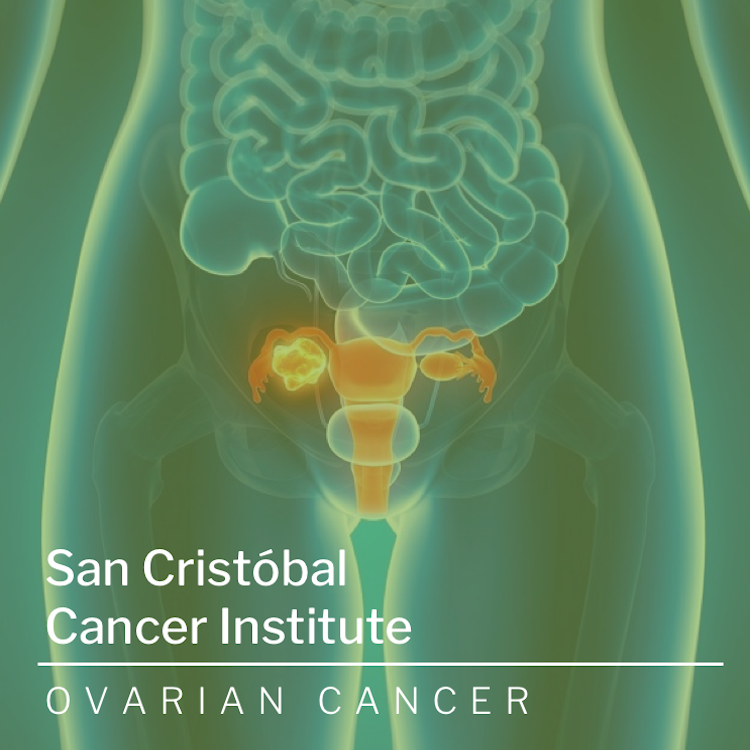
In most cases, ovarian cancer isn’t diagnosed until it has progressed to an advanced stage. In fact, according to the American Cancer Society, only about 20 percent of cases are diagnosed at an early stage. Typically, this is because ovarian cancer symptoms either aren’t apparent in the early stages of the disease or they mimic common stomach and digestive issues that are often mistaken for minor ailments. Women are more likely to experience symptoms once the disease has spread beyond the ovaries.
Overview
Ovarian cancer attacks the female reproductive system and unfortunately, it often goes undetected until it has spread within the pelvis and abdomen. At this late stage, ovarian cancer is more difficult to treat and is frequently fatal. Early-stage ovarian cancer, in which the disease is confined to the ovary, is more likely to be treated successfully. Surgery and chemotherapy are generally used to treat ovarian cancer.
Types
Different types of ovarian cancer are classified according to the type of cell from which they start:
- Epithelial tumors: About 90 percent of ovarian cancers develop in the epithelium, the thin layer of tissue that covers the ovaries. This form of ovarian cancer generally occurs in postmenopausal women.
- Germ cell carcinoma tumors: Making up about five percent of ovarian cancer cases, this type begins in the cells that form eggs. While germ cell carcinoma can occur in women of any age, it tends to be found most often in women in their early 20s. Six main kinds of germ cell carcinoma exist, but the three most common types are: teratomas, dysgerminomas and endodermal sinus tumors. Many tumors that arise in the germ cells are benign.
- Stromal carcinoma tumors: Ovarian stromal carcinoma accounts for about five percent of ovarian cancer cases. It develops in the connective tissue cells that hold the ovary together and those that produce the female hormones estrogen and progesterone. The two most common types are granulosa cell tumors and sertoli-leydig cell tumors. Unlike epithelial ovarian carcinoma, 70 percent of stromal carcinoma cases are diagnosed in Stage I.
- Small cell carcinoma of the ovary: Small cell carcinoma of the ovary (SCCO) is a rare, highly malignant tumor that affects mainly young women, with a median age at diagnosis of 24 years old. The symptoms are the same as other types of ovarian cancer.
Symptoms
Early-stage ovarian cancer rarely causes any symptoms. Advanced-stage ovarian cancer may cause few and nonspecific symptoms that are often mistaken for more common benign conditions.
Signs and symptoms of ovarian cancer may include:
- Abdominal bloating or swelling
- Quickly feeling full when eating
- Weight loss
- Discomfort in the pelvis area
- Changes in bowel habits, such as constipation
- A frequent need to urinate
Make an appointment with your doctor if you have any signs or symptoms that worry you. If you have a family history of ovarian cancer or breast cancer, talk to your doctor about your risk of ovarian cancer. Your doctor may refer you to a genetic counselor to discuss testing for certain gene mutations that increase your risk of breast and ovarian cancers.
Diagnosis
Tests and procedures used to diagnose ovarian cancer include:
- Pelvic exam. During a pelvic exam, your doctor inserts gloved fingers into your vagina and simultaneously presses a hand on your abdomen in order to feel (palpate) your pelvic organs. The doctor also visually examines your external genitalia, vagina and cervix.
- Imaging tests. Tests, such as ultrasound or CT scans of your abdomen and pelvis, may help determine the size, shape and structure of your ovaries.
- Blood tests. Blood tests might include organ function tests that can help determine your overall health. Your doctor might also test your blood for tumor markers that indicate ovarian cancer. For example, a cancer antigen (CA) 125 test can detect a protein that’s often found on the surface of ovarian cancer cells. These tests can’t tell your doctor whether you have cancer, but may give clues about your diagnosis and prognosis.
- Surgery. Sometimes your doctor can’t be certain of your diagnosis until you undergo surgery to remove an ovary and have it tested for signs of cancer.
Stages
Once it’s confirmed that you have ovarian cancer, your doctor will use information from your tests and procedures to assign your cancer a stage. The stages of ovarian cancer are indicated using Roman numerals ranging from I to IV, with the lowest stage indicating that the cancer is confined to the ovaries. By stage IV, the cancer has spread to distant areas of the body.
Treatment
Treatment of ovarian cancer usually involves a combination of surgery and chemotherapy.
Surgery: Operations to remove ovarian cancer include:
- Surgery to remove one ovary. For very early stage cancer that hasn’t spread beyond one ovary, surgery may involve removing the affected ovary and its fallopian tube. This procedure may preserve your ability to have children.
- Surgery to remove both ovaries. If cancer is present in both your ovaries, but there are no signs of additional cancer, your surgeon may remove both ovaries and both fallopian tubes. This procedure leaves your uterus intact, so you may still be able to become pregnant using your own frozen embryos or eggs or with eggs from a donor.
- Surgery to remove both ovaries and the uterus. If your cancer is more extensive or if you don’t wish to preserve your ability to have children, your surgeon will remove the ovaries, the fallopian tubes, the uterus, nearby lymph nodes and a fold of fatty abdominal tissue (omentum).
- Surgery for advanced cancer. If your cancer is advanced, your doctor may recommend chemotherapy followed by surgery to remove as much of the cancer as possible.
Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy is a drug treatment that uses chemicals to kill fast-growing cells in the body, including cancer cells. Chemotherapy drugs can be injected into a vein or taken by mouth. Sometimes the drugs are injected directly into the abdomen (intraperitoneal chemotherapy). Chemotherapy is often used after surgery to kill any cancer cells that might remain. It can also be used before surgery.
Targeted therapy: Targeted therapy uses medications that target the specific vulnerabilities present within your cancer cells. Targeted therapy drugs are usually reserved for treating ovarian cancer that returns after initial treatment or cancer that resists other treatments. Your doctor may test your cancer cells to determine which targeted therapy is most likely to have an effect on your cancer.
Palliative Care: Palliative care is specialized medical care that focuses on providing relief from pain and other symptoms of a serious illness. Palliative care specialists work with you, your family and your other doctors to provide an extra layer of support that complements your ongoing care. Palliative care can be used while undergoing other aggressive treatments, such as surgery, chemotherapy or radiation therapy. When palliative care is used along with all of the other appropriate treatments, people with cancer may feel better and live longer. Palliative care is provided by our skilled team of doctors, nurses and specially trained professionals, aimed at improving the quality of life for people with cancer and their families. This form of care is offered alongside curative or other treatments you may be receiving. Learn more about San Cristóbal Palliative Care.
Resources
San Cristobal Cancer Institute offers a wide array of options to help our patients feel calm and supported during the process of screening, diagnosis and treatment, as well as getting back to life after cancer. Browse our alternatives for patients – including financial aid for those eligible – in our Patient Resources section.
If you’d like to learn more about Ovarian Cancer through our San Cristóbal Education Resources, attend our events or learn about our Cancer Center, please contact us.
Knowledge is Power.
Education is one of our strongest tools at San Cristóbal Cancer Institute, empowering patients and their families with complete and updated information about more than a dozen types of cancer and providing first-hand knowledge through our dedicated team of cancer experts. If you’d like to know more, please get in touch with us. We look forward to offering you and your family powerful cancer awareness and the most comprehensive care.
